File Formats In The Printing
-
sentiment_very_satisfied
Viewers:
- 0
Whether for book printing or packaging printing. Not only because it can easily check the printing file on the screen, also it can dock with PS, AI, CDR and other file formats, to produce standard PDF format. Besides above advantages, use PDF file format for printing, also have other benefits, like PDFS are portable,PDFs are perfect size,PDFs are editable and maintain quality,etc.
The JPEG format became ideal for displaying images quickly and preserving better resolution. It is usually enough to save the image only once in JPEG format at the final stage of creation.
If you want to print images, especially high-quality images, TIFF format is a more suitable choice. But in TIFF files, none of the tools contain screen processing instructions. Screen processing is controlled by the program that prints the TIFF format file. If you want to save screen instructions along with bitmaps, you must use the EPS file format.
1. PDF (Portable Document Format)Characteristics: - Universally accepted format. - Preserves fonts, images, graphics, and layout. - Can include vector and raster images.
Best Uses: - Final print-ready files, brochures, posters, and digital proofs. |
2. JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)Characteristics: - Compressed raster image format. - Lossy compression results in reduced file size but can degrade image quality. - Widely supported and used for web and print.
Best Uses: - Photographs, web images, and quick proofs. |
3. TIFF (Tagged Image File Format)Characteristics: - High-quality raster image format. - Supports lossless compression. - Ideal for detailed images and complex graphics.
Best Uses: - High-resolution images, detailed graphics, and archival purposes. |
4. PSD (Photoshop Document)Characteristics: - Native file format for Adobe Photoshop. - Supports layers, masks, and a wide range of editing features. - Maintains high image quality.
Best Uses: - Complex image editing, retouching, and projects requiring extensive editing capabilities. |
5. EPS(Encapsulated PostScript)Characteristics: - Vector format used for high-resolution graphics. - Scalable without loss of quality. - Can include both vector and raster elements.
Best Uses: - Logos, illustrations, and graphics requiring scalability. |
6. DCS (Desktop Color Separations)Characteristics: - Variant of the EPS format. - Allows for the separation of images into CMYK or spot color channels. - Useful for high-end color printing.
Best Uses: - Projects requiring precise color separations for printing. |
7. AI (Adobe Illustrator)Characteristics: - Native file format for Adobe Illustrator. - Supports vector graphics, layers, and a range of editing features. - Ideal for creating scalable illustrations and graphics.
Best Uses: - Logos, illustrations, and any vector-based artwork. |
8. CDR (CorelDRAW)Characteristics: - Native file format for CorelDRAW. - Supports vector graphics, layers, and a range of editing features. - Similar in functionality to AI files.
Best Uses: - Vector graphics, illustrations, and designs created using CorelDRAW. |
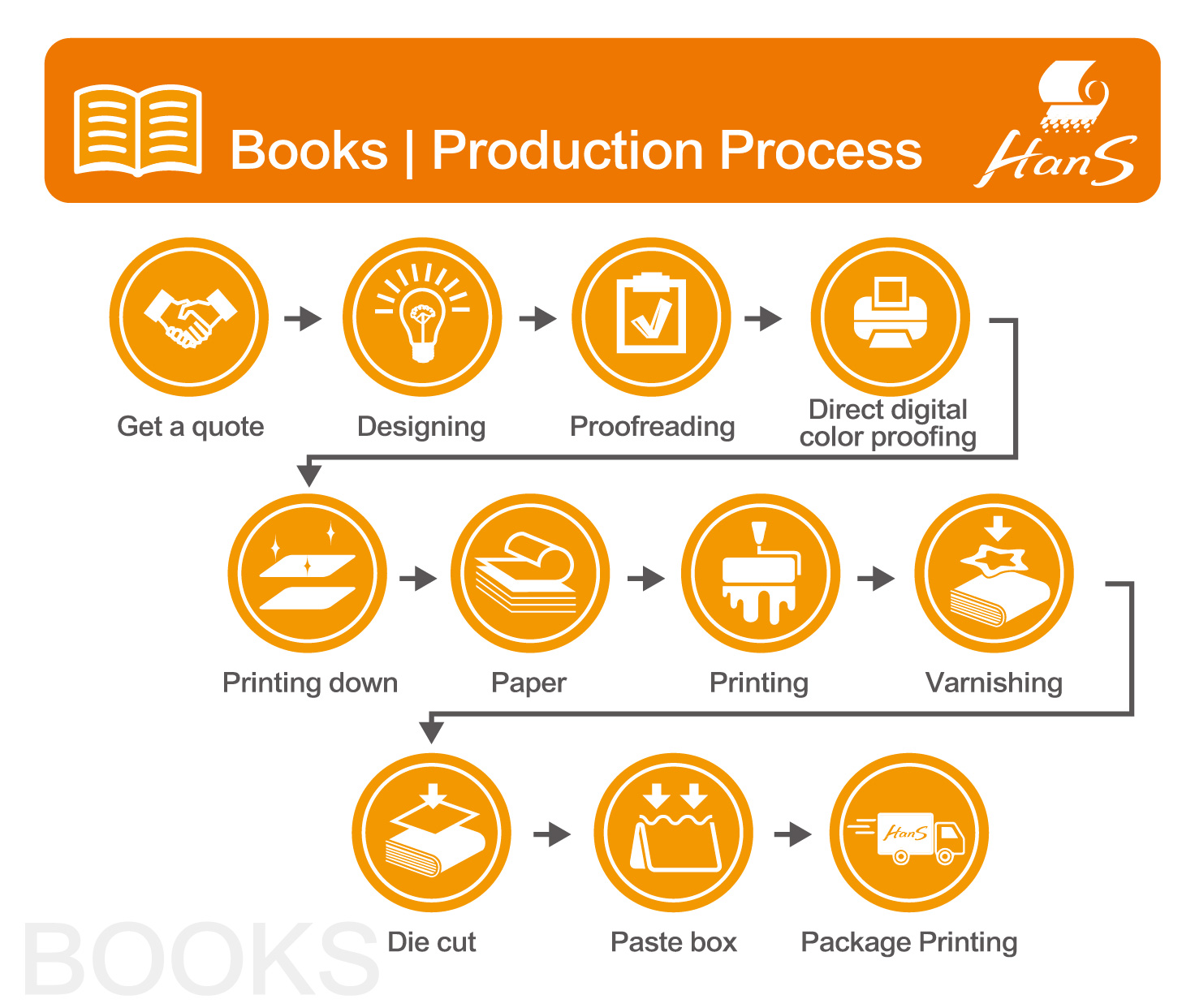
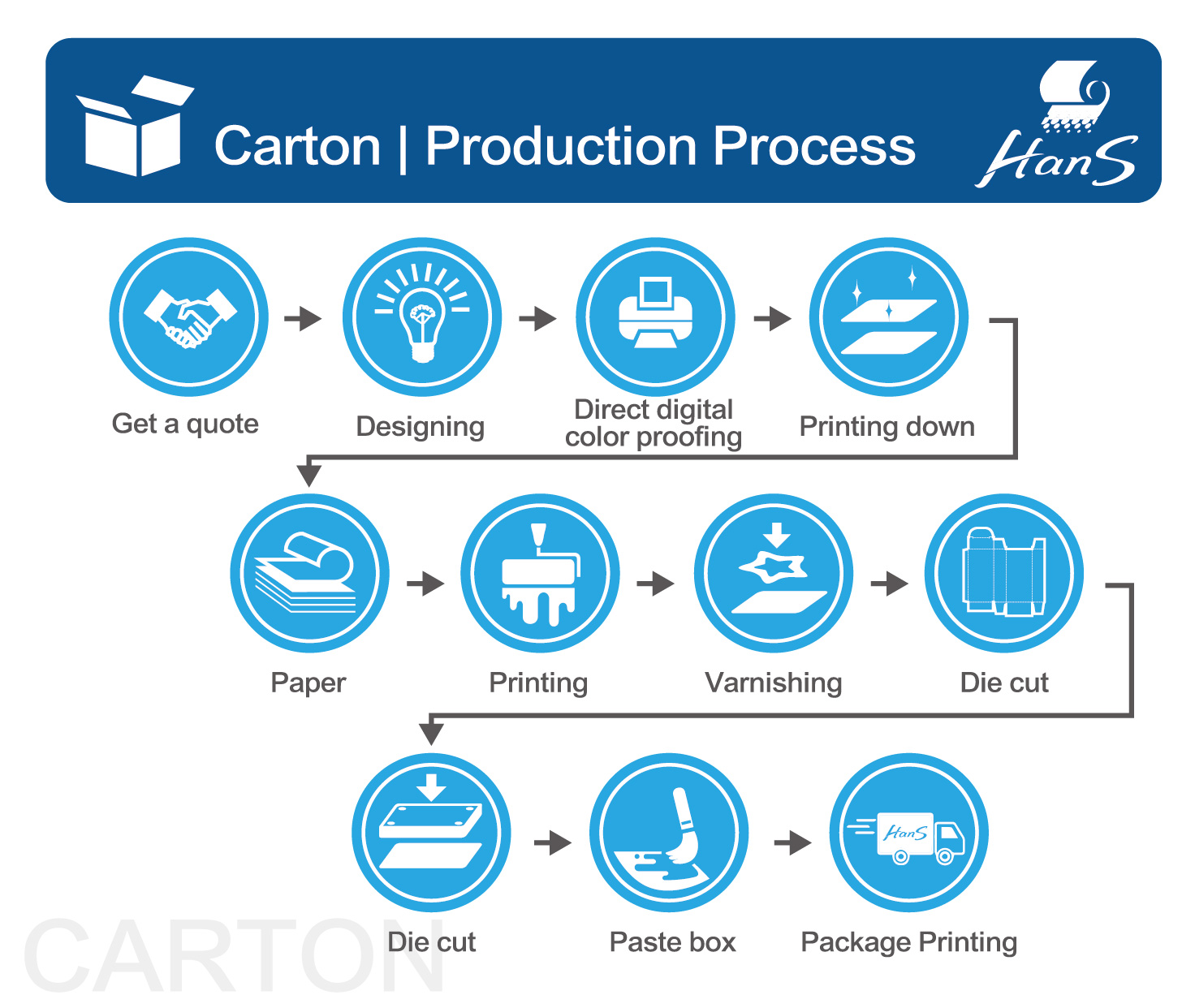
From planning and filing to the completion of printed matter, printing must go through many procedures, combined with the professional skills of countless people, such as graphic designers, commercial photographers, copywriters, typewriters, artists, color separation technicians, printing technicians, Public workers, printing technicians, bookbinding, varnishing and various processing technicians, etc., without any one, can not successfully complete the printed matter, so they are all important contributors.
We assist many enterprises and organizations in the integrated planning and production of printed materials, focusing on providing comprehensive printing integration services, helping you think more, do more, and win more under limited time and money.